RoStep RwStep RoRanAd RwRanAdr ChgWrite
Sequencer/Array Property Dialog
Sequencer and array modules are very similar. Their function is to access and sequence values stored in a memory array. Array modules use global memory arrays, and therefore an array module can share its sequence data with any number of other array modules. Sequencer modules have their arrays stored with the module, so their sequence data is private to the module.
Most ArtWonk sequencer and array modules are nearly identical. The main difference between them is that Array modules have an additional input, which specifies the array number handle (Ary#). Array modules have the same names as the corresponding Sequencer modules, but the name starts with "A," as in the "RoStep" sequencer module and the "ARoStep" array module.
Memory arrays used by sequencer and array modules may be of any practical size. The default size is 128 elements, numbered 0-127. Use the Properties pop up button on the upper right of the module to change the sequence size and to initialize it with various fills such as counts, scales, or random values.
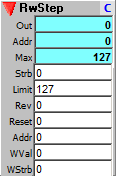
This is the standard step sequencer module that increments or decrements to the next step on each strobe input.
Outputs:
Out: value at the current step (read address)
Addr: The current step address. This is incremented or decremented by the Strobe input; the address increments from 0 to the Limit value, then rolls over to 0 again. If reverse, it decrements from the Limit value to 0.
Max: Address of maximum step.
Inputs:
Strb: Strobe (0 to NZ transition) to step to the next address.
Limit: Sets the upper limit of the count, the point at which it rolls over back to 0. This should be a value less than the allocated memory size (Max).
Rev: Reverse direction of count. Set to non zero to decrement, 0 to increment.
Reset: Resets the current step address to the value set by Addr, below.
Addr: Dual purpose input. Sets the reset address and sets the write address when writing values to the sequence.
WVal: Value to write into the sequencer memory array upon receipt of WStrb.
WStrb: 0 to NZ transition writes WVal input to address given by Addr input (not to current step address)
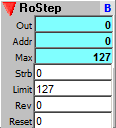
A step sequencer as above, but without the capability of writing. Use the property dialog to set memory contents.
Outputs:
Out: value at the current step (read address)
Addr: The current step address. This is incremented or decremented by the Strobe input; the address increments from 0 to the Limit value, then rolls over to 0 again. If reverse, it decrements from the Limit value to 0.
Max: Address of maximum step.
Inputs:
Strb: Strobe (0 to NZ transition) to step to the next address.
Limit: Sets the upper limit of the count, the point at which it rolls over back to 0. This should be a value less than the allocated memory size (Max).
Rev: Reverse direction of count. Set to non zero to decrement, 0 to increment.
Reset: Resets the current step address to 0 if counting forward, or Limit if counting backward.
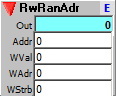
Directly addressable sequencer. Has separate address inputs for read and write, to allow read/write operations such as delay sequencing. The Addresser clock module is especially useful for addressing this sequencer.
Output:
Out: Sequencer value addressed by the Addr input.
Inputs:
Addr: Address of sequencer step to send to output.
WVal: Value to write to WAdr address.
WAdr: Write address.
WStrb: Strobe writes value input to current write address.
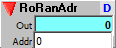
Directly addressable read only sequencer.
Output:
Out: Sequencer value addressed by the Addr input.
Inputs:
Addr: Address of sequencer step to send to output.
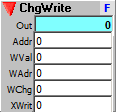
Directly addressable sequencer. Has separate address inputs for read and write, to allow read/write operations such as delay sequencing. This is similar to the RwRanAdr sequencer, but it writes on change at the Chng input, rather than strobe.
Output:
Out: Sequencer value addressed by the Addr input.
Inputs:
Addr: Address of sequencer step to send to output.
WVal: Value to write to WAdr address.
WAdr: Write address.
WChg: Strobe writes value input to current write address.
XWrit: (Exclusive Write), erases the previous value while writing the current value.
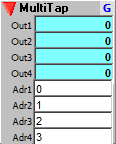
Directly addressable read only sequencer with adjustable multiple address and output pairs. Set the number of input/output pairs with the Tap control in the Properties dialog.
Outputs:
Outn: Sequencer value addressed by the corresponding Addr input.
Inputs:
Addrn: Address of sequencer step to send to output corresponding.
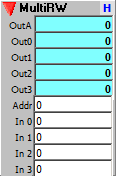
Directly addressable read/write sequencer with both directly addressable output and individual input and output pairs for each stage. Set the number of input/output pairs with the Tap control in the Properties dialog.
This module is ideal for creating step sequencers that uses knobs or sliders to set stage values.
Outputs:
OutA: Sequencer value addressed by the Addr random address input.
Outn: Value of the nth stage.
Inputs:
Addr: Address of sequencer step to send to OutA output.
In n: Value to write to the nth stage. Only writes when the value changes.
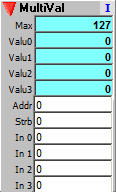
Multi value table sequencer steps through sets of values. Typically used to access groups of setup values, such as the 3-4 initialization constants most Fractal Modules require.
Use the Sequencer/Array Property Dialog to set the number of simultaneous values (#Taps up/down control in the lower left) and the number of sequence elements (Max Addr setting). The actual number of value sets will be the number of sequence elements divided by the number of simultaneous values.
For example, if you need 4 simultaneous elements, and you want to have 10 groups of them, you would need 40 sequencer elements total. So you would set the Max Addr to 39, then click on the Udate The Fill button to set the value. When you dismiss the Property Dialog, the module Max output will be set to 9, showing you have 10 sets (addressed 0 to 9) of 4 values.
Outputs:
Max: Maximum value table address. The actual total sequence elements will be the number of Value outputs times Max+1 (+1 because Max represents the steps numbered from 0).
Valuen: Value of the nth stage.
Inputs:
Addr: Address of group of values to send to the Value outputs.
Strb: Strobe to copy the value inputs to the sequencer memory, and thus to the Value outputs..
In n: Value to write to the nth stage. Only writes upon strobe.
This module allows you to access the private memory in another Sequencer module. It has no sequencer memory of its own. When connected to any other Sequencer, it acts similar to a RoRanAdr sequencer, but the memory it reads is the host sequencers. This module is for Sequencer modules only, not for Array modules - which allow shared memory simply by addressing the same array number.
Output:
Out: Sequencer value addressed by the Addr input.
Inputs:
Addr: Address of host sequencer step to send to output.
From: Sequencer module to read from. Just plug an output from the host sequencer into this input, and the connection will automatically be made on the next Reset.
Creates a Snapshot table of a sequencer, and automatically processes Snaps for it.
Sequencers are not normally processed by Snapshot because snapshots need to store 128 copies of the value to be saved and restored; since sequencer arrays can be any size, automatically saving 128 copies of them would quickly use up the computer's memory resources.
With this module you can connect just the sequencers you need to have saved and restored via the Snapshot. It is a set and forget module; once connected the Snapshot processing is automatic.
Output:
Size: Number of elements in target sequencer, 0 if error.
Input:
Seq: Target sequencer to Snapshot; use any output from the sequencer module to connect.
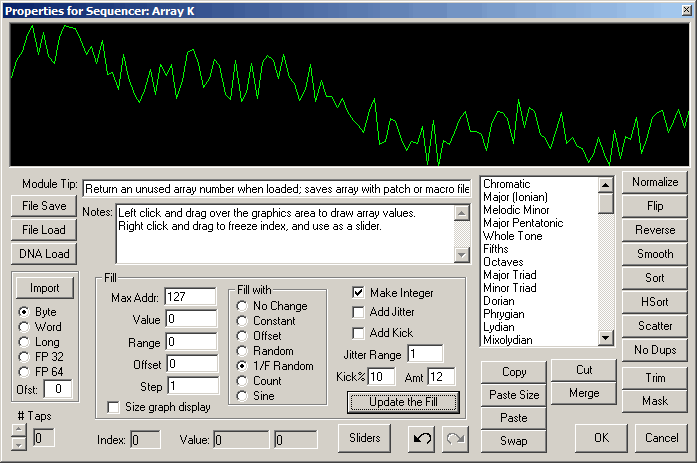
Sequencers and Arrays have a Property button, the blue priority label (A., B, C...) in the upper right corner of the module. Click it to pop up the priority dialog.
The main purpose of the sequencer property dialog is to initialize sequencer arrays. You can change the size of an array here, and you can initialize it with various numerical patterns.
The top area of the dialog is a graphical trace of the sequencer values. If it is a new sequencer this area will be blank, as new sequences are initialized to 0 when first created.
You can draw values directly into the array by left click and drag in the graphics area; to freeze the index value so the mouse acts as a slider, right click and drag in the graphics area.
Initializing Sequencer/Array memory
To change the memory size, type in the Max Adr value you want, and click on the "Update the Fill" button. You can choose to initialize memory to specific values or runs of values by selecting the "Fill With" option prior to selecting "Update the Fill" or you can do it anytime later. Just remember to click the update button to make the selection happen. You will see the results of the update in the top graphical display.
At any time, you can also perform several memory options, such as reversing the order, or sorting the values. Just click the appropriate buttons and the results will show up in the graphics display. Each button has a tool tip that specifies what it does and what parameters need to be set, if any.
Sliders
The Sliders button pops up a set of 24 sliders that can access up to the first 128 sequencer values, with an integer range of 0-127. Use the sliders for easy, accurate data entry for typical MIDI range values.
Importing and exporting sequences
You can move sequences around among sequencer and array modules, and import numerical data from other sources.
To move a sequence from one module to another, use the Copy and Paste buttons. Copy stores the current sequence into a sequencer clipboard; Paste copies from the clipboard to the current sequencer. To exactly paste a sequence, which may involve resizing the current sequence to match the sequence that had been pasted to the clipboard, use Paste Resize; to paste only the amount of data that fits into the current sequencer, without resizing the current sequencer, use Paste (you don't need to memorize this, the tool tips on the buttons describe their functions).
The array Copy/Paste clipboard is also used by the PitchMap module, so in addition to moving sequences among sequencer and array modules, you can use Copy and Paste to move them into and out of PitchMap modules.
To import data from other source use the Import button, which pops up a file open dialog. Prior to opening the file for import, specify the numerical format of the data source from the option buttons. Only numerical data is supported, however if you need to import text or data base data, you can first convert it to a numerical format with the DataBin dialog available from the ArtWonk main menu.
You can also save and load ArtWonk array (.awa) files with the Save and Load buttons. The .awa format is compatible with both sequencer and array files and with the array functions in the Function module.
ArtWonk is Copyright © 2003-2014 by John Dunn and Algorithmic Arts. All Rights Reserved.